Page 82 - Enchiridion 4.0 program_EN
P. 82
Strategic Partnerships for school education 2019-1-PL01-KA201-065137
Project: Teacher4.0 - comprehensive method of implementation of Industry 4.0
concept into didactic practice in primary and secondary schools
7. Finally, we can paint with a brush, airbrush or spray, and coat our model with epoxy resin or metal.
What is the FDM method?
The main reason for the creation of 3D printing and the association with it and the use of FDM
technology in it was the rapid creation of prototypes at low-budget expenditures available to the
average person. Thanks to this technology and making it available to a wide group of users, it began
to be improved and used to produce final models.
FDM technology, i.e. one of the incremental printing techniques that uses thermoplastics in the
printing process, the characteristic feature of which is the extrusion of material from the printing
heads. Models created thanks to this technology are made of plastics (in the form of a line with a
constant diameter), forming the geometry by heating the material to a semi-plastic state and then
pushing it through the printer nozzle. The "filament" that is pushed out, as it is popularly called, has a
diameter of 1.75mm to 2.85mm and is unwound from a spool suspended on the printer. Currently,
FDM technology is the most widely used among all incremental methods in the world. It uses
materials such as ABS, ASA, PC, PC-ABS and ULTEM. The first developers of the FDM technology is
Stratasys®, as an alternative name FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) was introduced.
The principle of operation of the FDM / FFF technology
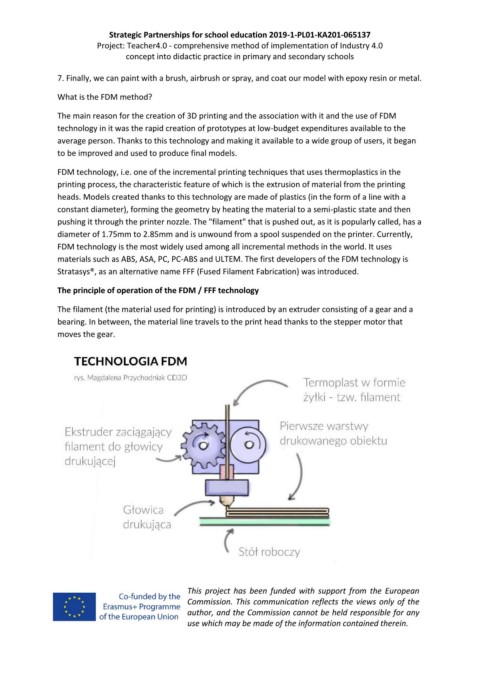
The filament (the material used for printing) is introduced by an extruder consisting of a gear and a
bearing. In between, the material line travels to the print head thanks to the stepper motor that
moves the gear.
This project has been funded with support from the European
Commission. This communication reflects the views only of the
author, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any
use which may be made of the information contained therein.